Cheilosia ranunculi Doczkal, 2000
Identification
Identification difficulty = 3. ![]()
![]() according to Ball & Morris, 20241
according to Ball & Morris, 20241
Synonymy
This species and C. albitarsis were separated by Doczkal (2000)2.
Biology
There is currently very little information on the biology of this species. The larva is unknown, although it is probablt associated with buttercups Ranunculus like its close relative, C. albitarsis. Adults are usually found visiting buttercup flowes.
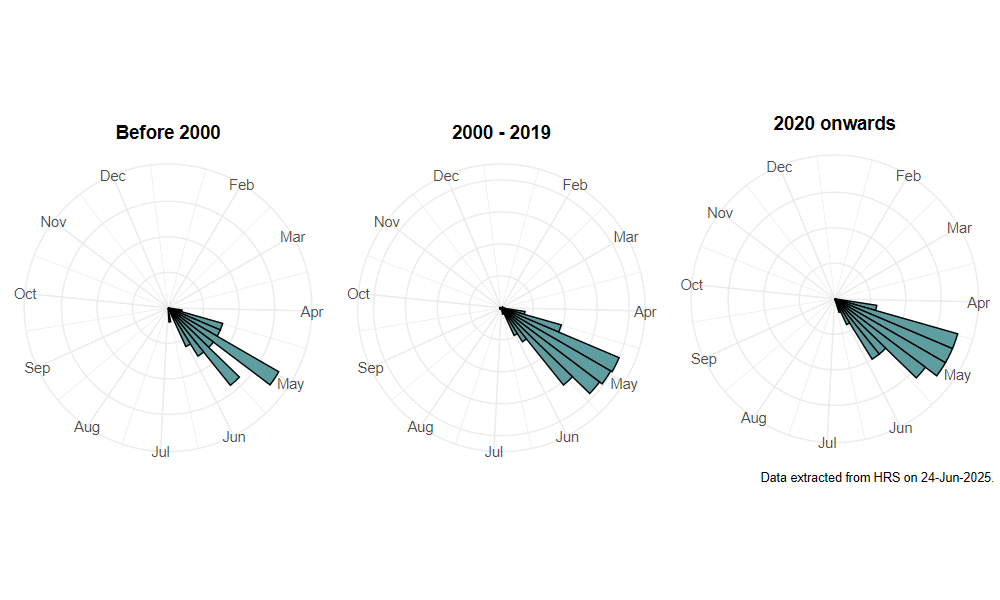
Flight period
The following plots show the number of unique records per week excluding those reported to be of immature stages.
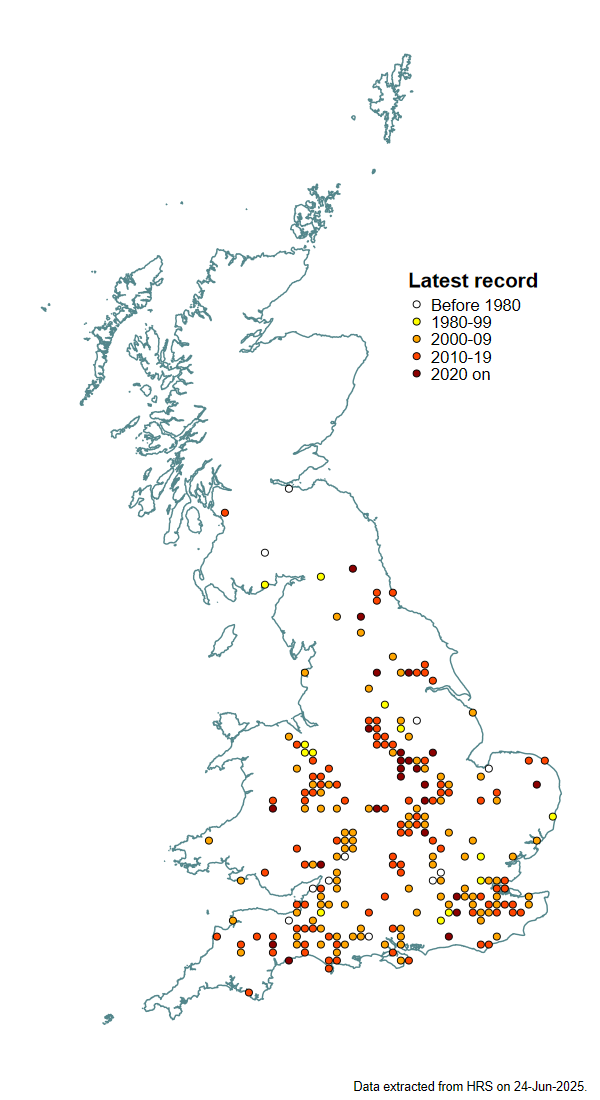
Distribution
This is a southern species that mainly occurs south of the Tees and seems to be scarce in northern England. It was added to the Scottish list by Rotheray & Wilkinson (2010)3 who listed some old records from as far north as Edinburgh based on re-examination of specimens in the collections of the National Museum of Scotland.
Trends
The following plots show the Frescalo TFactor vs year and a map of the rescaled frequency (all records) for the species.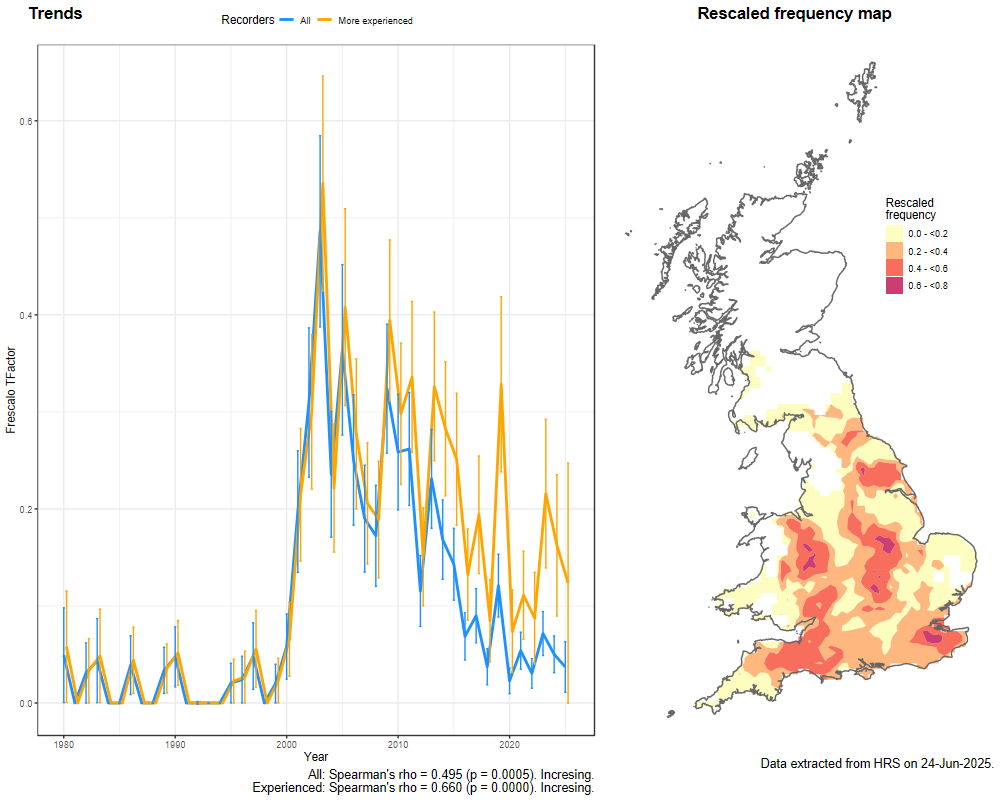
-
Ball, S., & Morris, R. (2024). Hoverflies of Britain and Ireland. WILDGuides (3rd ed.). Oxford: Princeton University Press. ↩
-
Doczkal, D. (2000). Description of Cheilosia ranunculi spec. nov. from Europe, a sibling species of C. albitarsis Meigen (Diptera, Syrphidae). Volucella, 5, 63–78. ↩
-
Wilkinson, G. (2010). Cheilosia psilophthalma Becker and Brachypalpus laphriformis (Fallén) (Diptera, Syrphidae) new to Scotland. Dipterists Digest (Second Series), 17, 165–167. ↩