Neoascia obliqua Coe, 1940
Identification
Identification difficulty = 3. ![]()
![]() according to Ball & Morris, 20241
according to Ball & Morris, 20241
Biology
The larva of this species remains unknown, but other members of the genus are semi-aquatic, inhabiting accumulations of wet, organic matter. Found amongst lush vegetation in marshes and water margins in sheltered locations, such as at the edges of wet woods and wooded streams.
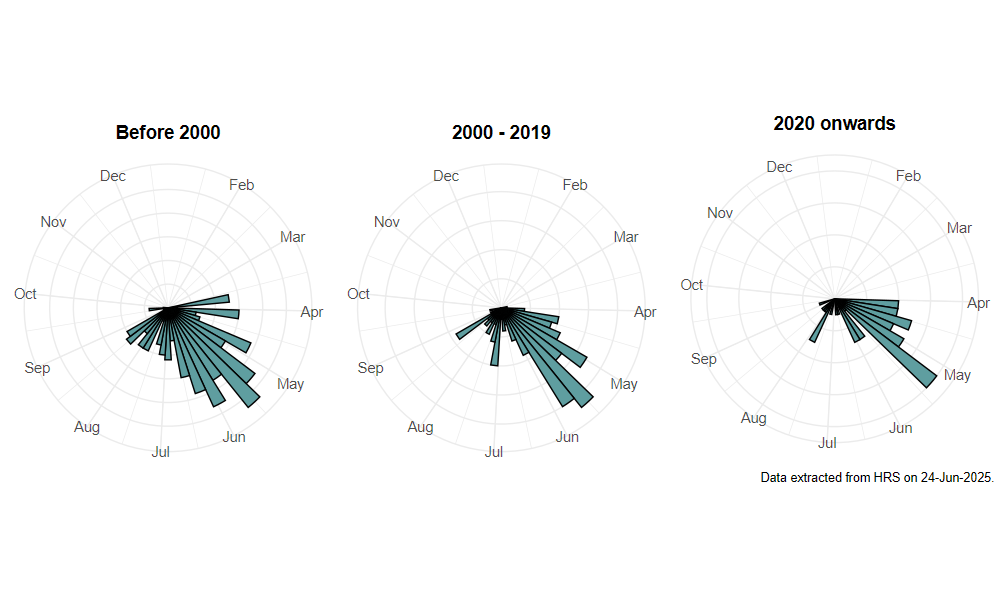
Flight period
The following plots show the number of unique records per week excluding those reported to be of immature stages.
Status
Was listed as 'Notable' by Falk, 19912, but dropped from this status by Ball & Morris, 20143 who consider it LOWER RISK.
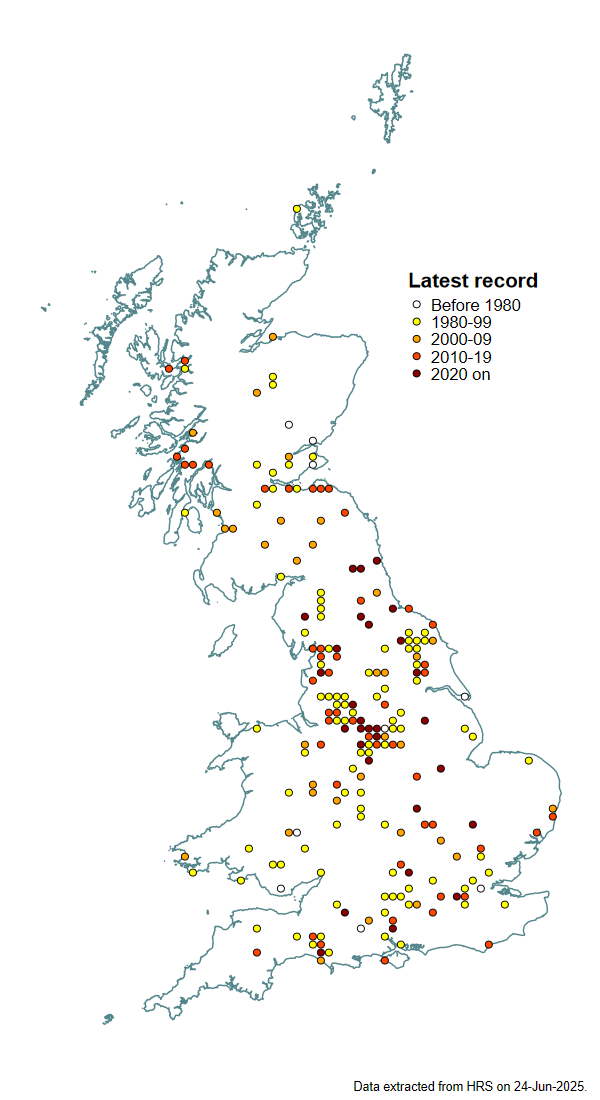
Distribution
Widely distributed but generally scarce, with most records from northern England and Scotland. It appears to be particularly associated with beds of Butterbur Petasites hybridus and can be found in these situations when specifically sought. This recording technique has led to an increase in our knowledge of its distribution which is mainly northern and western, especially in the Pennines.
Trends
The following plots show the Frescalo TFactor vs year and a map of the rescaled frequency (all records) for the species.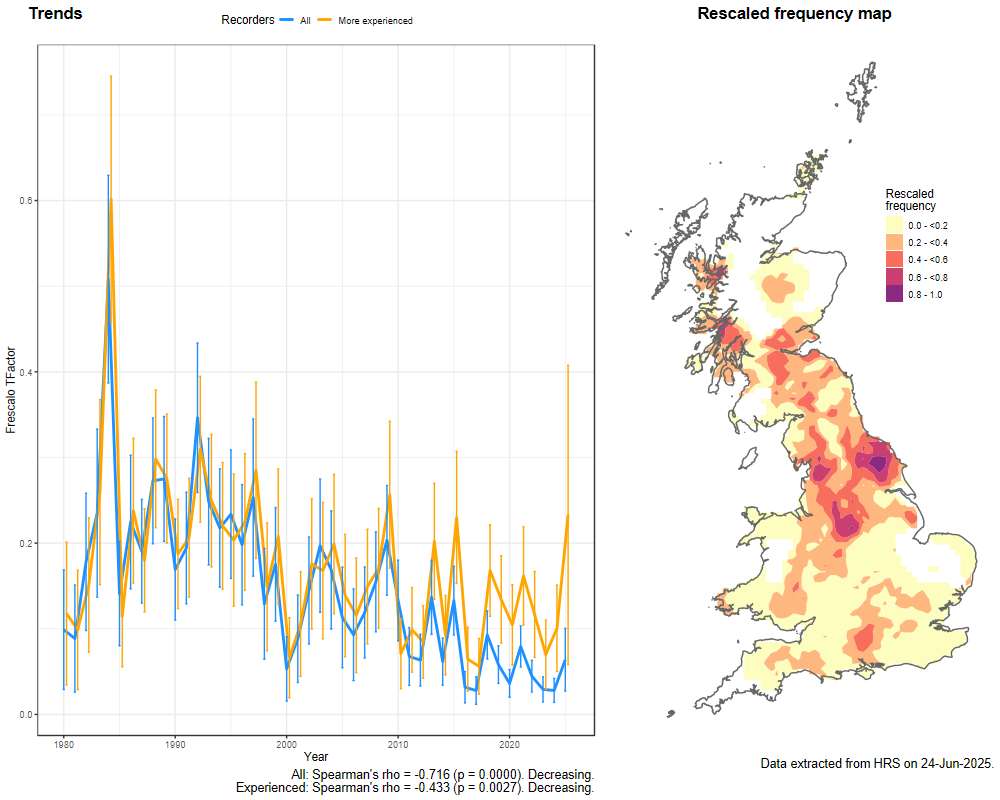
-
Ball, S., & Morris, R. (2024). Hoverflies of Britain and Ireland. WILDGuides (3rd ed.). Oxford: Princeton University Press. ↩
-
Falk, S. (1991). A review of the scarce and threatened flies of Great Britain. ( No. 39). Research and Survey in Nature Conservation (pp. 1–194). Peterborough: NCC. ↩
-
Ball, S., & Morris, R. (2014). A review of the scarce and threatened flies of Great Britain. Part 6: Syrphidae. ( No. 9). Species status (pp. 1–130). Peterborough: JNCC. ↩