Scaeva selenitica (Meigen, 1822)
Identification
Identification difficulty = 2. ![]()
![]() according to Ball & Morris, 20241
according to Ball & Morris, 20241
Biology
The larva feeds on aphids on Pine Pinus sp. and Spruce Picea sp. A puparium has been found under the bark of Spruce. Records that make reference to habitat most frequently specify woodland (including both deciduous and coniferous), although open habitats, such as chalk grassland, are also mentioned. In the south of England this species is mainly associated with pine plantations on heathland. Adults are often seen visiting flowers, such as white umbels, along woodland rides and edges and males hover in clearings.
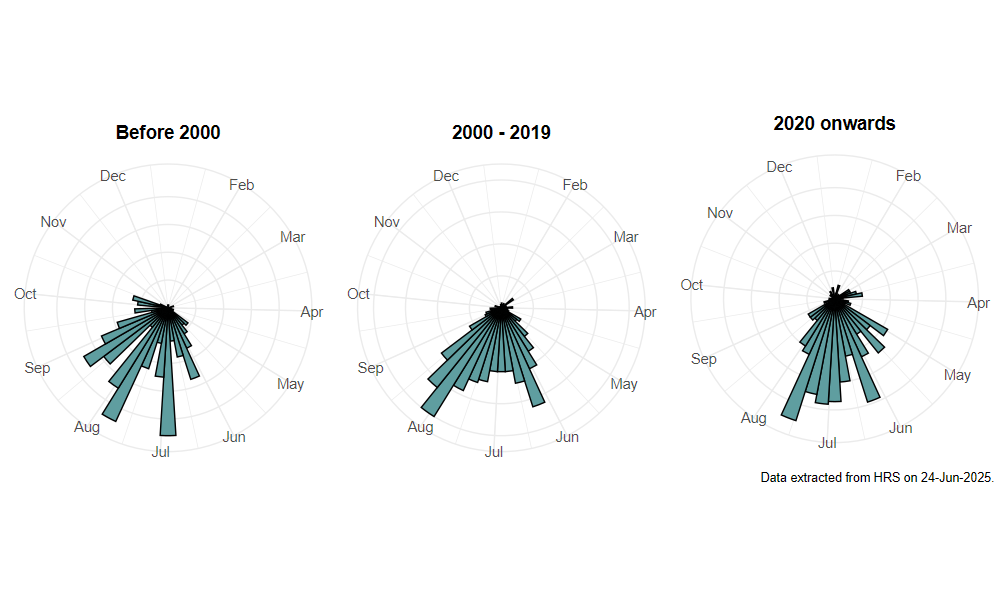
Flight period
The following plots show the number of unique records per week excluding those reported to be of immature stages.
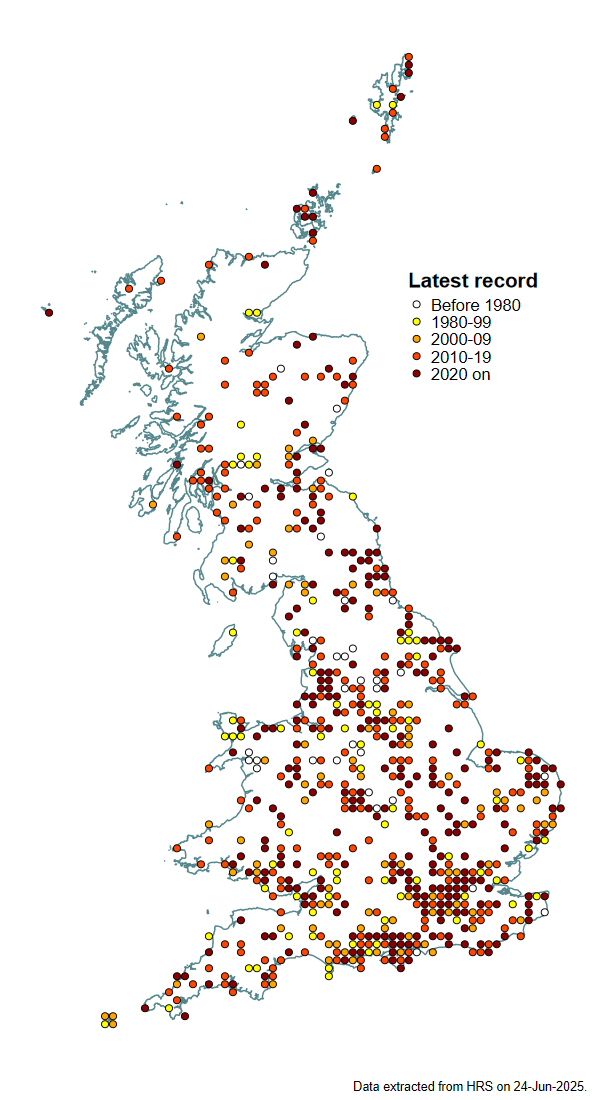
Distribution
Scarce but widely scattered. Whilst Stubbs & Falk (1983)2 state that it is at least a partial migrant, Falk (1991)3 argues that it is resident. There have been several very early spring records recently that suggest over-wintering by adults. It is quite possible that a resident population receives reinforcement by migration from the continent.
Trends
The following plots show the Frescalo TFactor vs year and a map of the rescaled frequency (all records) for the species.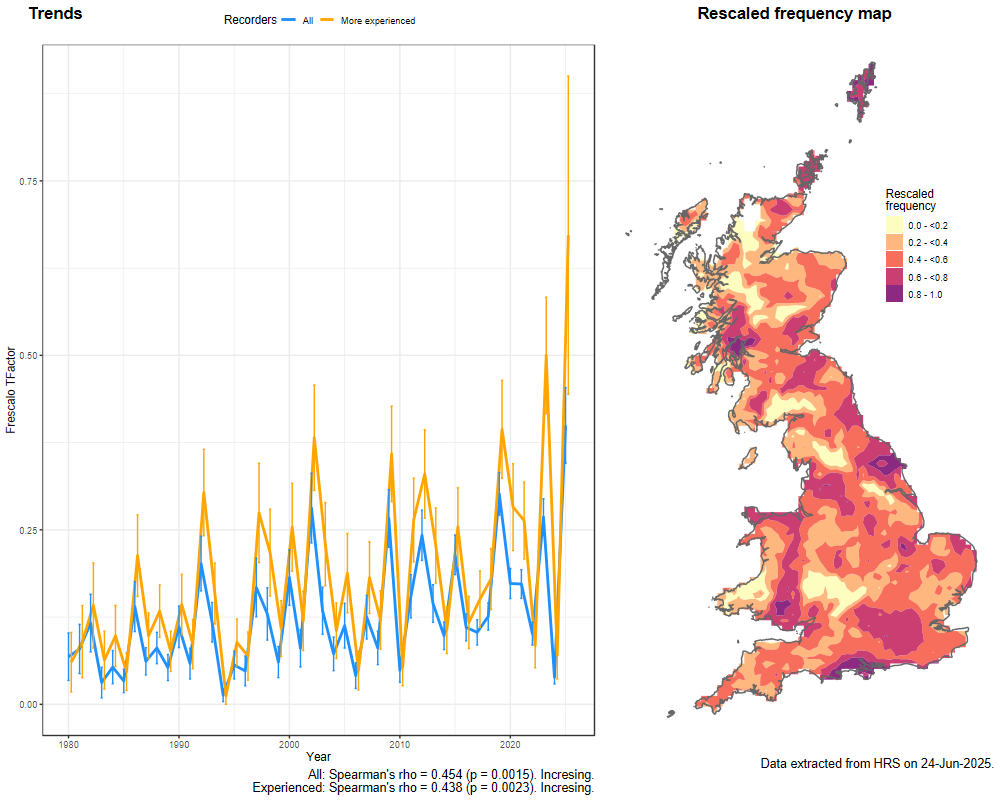
-
Ball, S., & Morris, R. (2024). Hoverflies of Britain and Ireland. WILDGuides (3rd ed.). Oxford: Princeton University Press. ↩
-
Stubbs, A., & Falk, S. (1983). British Hoverflies: An Illustrated Identification Guide (1st ed.). Reading: BENHS. ↩
-
Falk, S. (1991). A review of the scarce and threatened flies of Great Britain. ( No. 39). Research and Survey in Nature Conservation (pp. 1–194). Peterborough: NCC. ↩